Mastersizer Anwenderhandbuch
Version number: MAN0675-03-DE
Access support to accelerate your scientific discovery with grants of up to $20K or $50K, or up to 50% off. Apply to our Academic Grant Program now
Apply to our Academic Grant Program now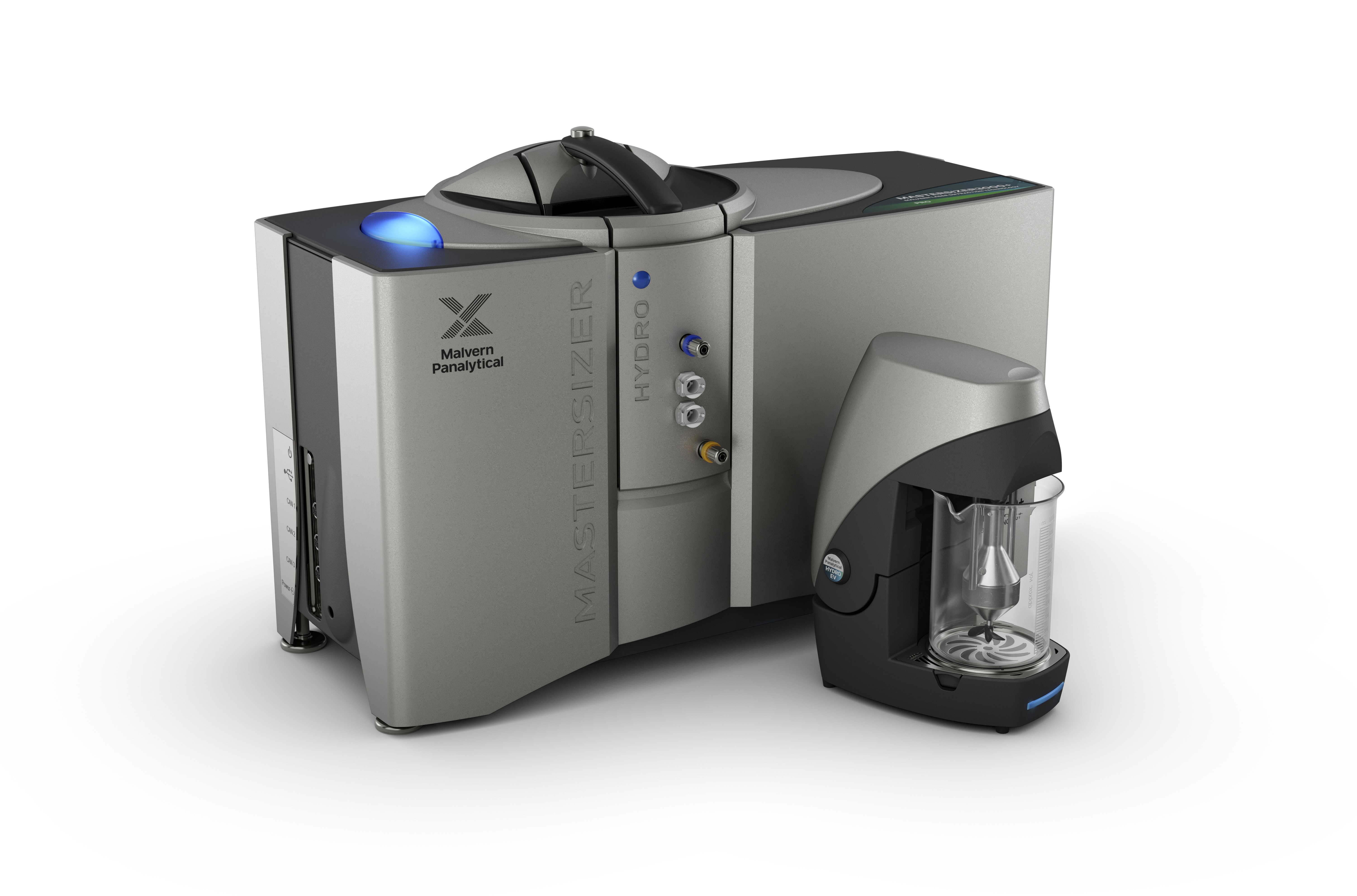



Looking for more information?
To request a quote, more information or download a brochure select an option below.
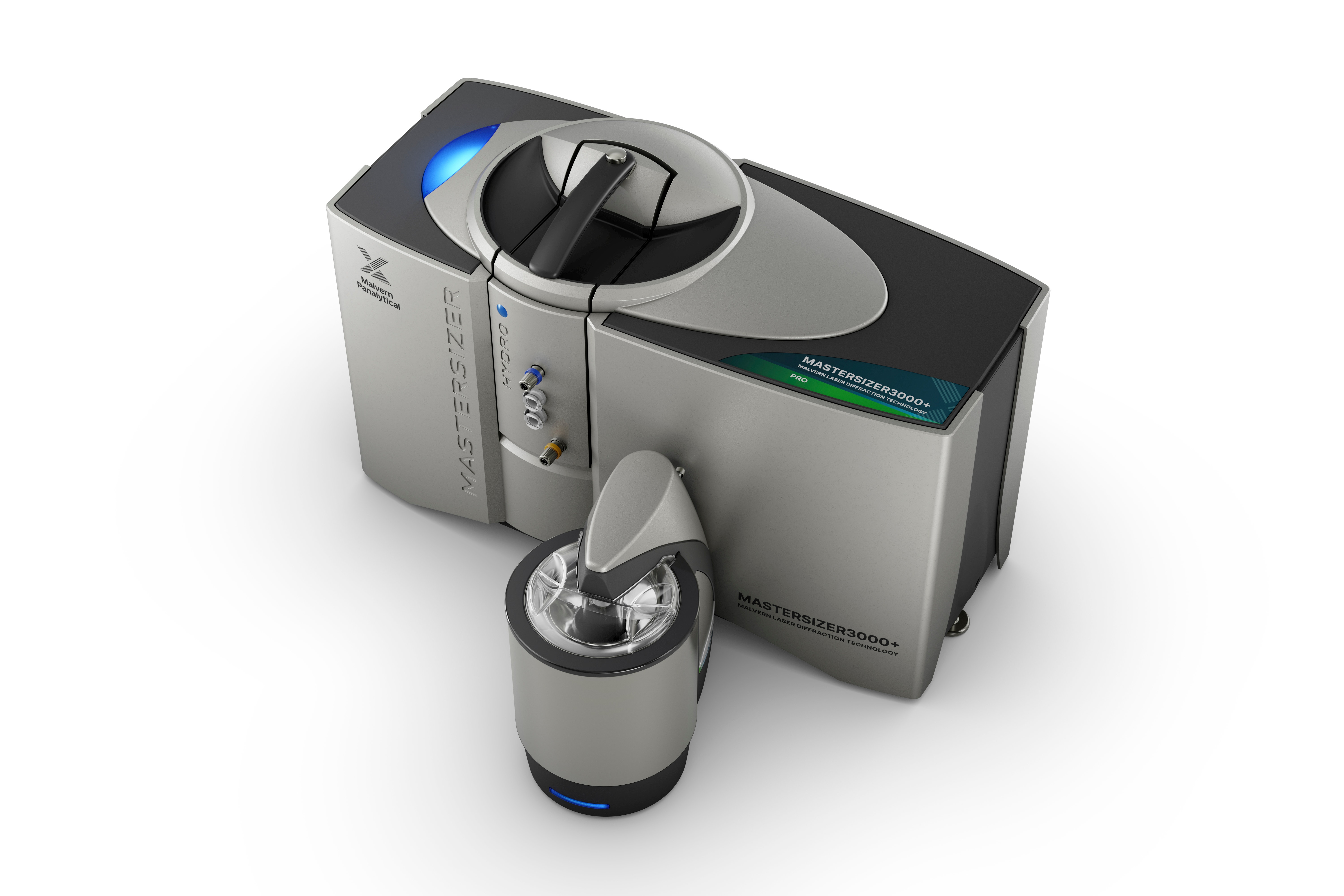
The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro generates the highest quality data for applications needing micron-scale sizing capabilities and the advanced software options of Mastersizer Xplorer.
 Works with OmniTrust: Malvern Panalytical's compliance solution for the regulated environment
Works with OmniTrust: Malvern Panalytical's compliance solution for the regulated environment

The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro uses the technique of laser diffraction to measure the particle size and particle size distribution of materials.
It does this by measuring the intensity of light scattered as a laser beam passes through a dispersed particulate sample.
This data is then analyzed to calculate the size of the particles that created the scattering pattern.
Three main elements enable the system to consistently and reliably deliver the accurate, robust particle sizing data that is central to the effective operation of so many industrial processes.
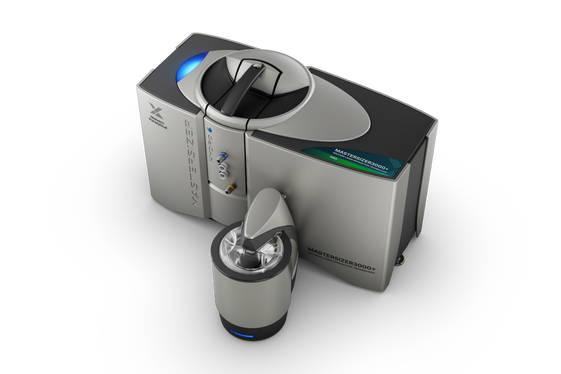
The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro takes measurements from 0.1 to 2500 µm using a single optical measurement path, making it suitable for an extremely wide range of applications.
The dispersed sample passes though the measurement area of the optical bench, where a laser beam illuminates the particles. A series of detectors then accurately measures the intensity of light scattered by the particles within the sample for red light wavelengths and over a wide range of angles.

The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro comes with a choice of six wet dispersion accessories to handle an extended range of sample volumes and a wide variety of dispersants.
A state-of-the-art dry dispersion system enables rapid and reproducible powder dispersion, even for more fragile materials.
Sample dispersion units ensure that particles are delivered to the measurement area of the optical bench at the correct concentration and in a suitable stable state of dispersion to ensure accurate, reproducible measurements.

Mastersizer Xplorer software meets the growing demand for easy-to-use instruments that deliver excellent results without constant input from experts.
The software controls the system during the measurement process, analyzing scattering data to calculate a particle size distribution. Its intuitive interface guides users through every stage of the process, from selecting a robust method through to routine measurement and result reporting.
In-built expert advice on method development, method performance and results quality reduces training requirements and makes particle size analysis simpler and faster.

Powder flowability is important in maintaining manufacturing efficiency for many processes. Inconsistent powder flow can directly affect product quality variables such as the content uniformity of pharmaceutical dosage forms, or may lead to process variability as powder feed inconsistencies change the effectiveness of particle size reduction processes. Powder flow is a critical consideration in the manufacture of sintered products using additive manufacturing or 3D-printing techniques. Here, poor flow during powder bed deposition may lead to variations in powder bed density, resulting in defects that reduce the strength of the finished part.
Particle size and particle size distribution analysis are critical to understanding the flow properties of a powder, since these characteristics help predict how particles within the powder will pack and lock together. Powders that have a large particle size with a narrow size distribution tend to exhibit good flowability. Those with a small particle size, or a broad particle size distribution, tend towards poorer flowability because of the greater surface area of contact that exists between the particles and the ability of the fine particles present to fill the voids.
The packing density of particles influences the success of many processes, including mold-filling in ceramic and metal component production, powder coating, and the solids loading of suspensions. The way that particles pack together is a function of both their size and size distribution. Larger particles pack less efficiently than smaller ones, creating bigger voids. Broadening the particle size distribution improves packing efficiency by allowing smaller particles to pack the spaces between larger ones. Minimizing voidage is crucial to producing flaw-free sintered components. In powder coating, close packing enables efficient melting at lower temperatures, giving more time for cross-linking reactions between polymer particles for a better finish.
Particle packing also influences the rheology of suspensions, principally their viscosity. A mix of large and small particles has the least impact on the viscosity of the system because of their greater packing efficiency, a phenomenon that can be exploited to increase the solids loading of suspensions such as paints and ceramics.
The stability of suspensions and emulsions used and produced in industries such as pharmaceuticals and foods is important in ensuring product efficacy, acceptability, and success. Dispersion stability and gravitational separation are both key elements.
Dispersion stability: Achieving a stable dispersion requires control of the forces of adhesion and cohesion that exist between particles within a medium. These forces can lead to flocculation of emulsions or the creation of agglomerates within suspensions and powders. The risk of poor dispersion stability increases with decreasing particle size and can significantly impact processing. It may lead to powder conveyance issues within manufacturing processes, or problems with final product performance, such as the formation of agglomerates that give rise to imperfections in coatings and paints. Particle size and particle size distribution analysis is used in the management of dispersion stability risk and to identify the impact of stability problems on product performance and acceptance.
Gravitational separation: Improving the stability of a suspension or emulsion to gravitational separation relies on balancing the gravitational pull on the particles, a function of particle size and density, with the up-thrust of the suspending fluid, which depends on viscosity. In emulsions, particle size analysis is used to assess the likelihood of creaming, to which larger droplets are prone, and to monitor stability to flocculation and coalescence over time. Since droplet size and the degree of flocculation may also affect characteristics such as the mouthfeel of a food or the viscosity of a drink, particle size should be measured routinely when optimizing and manufacturing emulsion formulations.
The viscosity and flow of suspensions and slurries depend on different physical properties, including particle size and particle size distribution. If particle size decreases (for a constant volume fraction) and/or the size distribution increases, the sample viscosity will increase and the sample will flow less readily. Viscosity is important for many applications such as paints, cosmetics and battery manufacture. Take batteries, for example, where the battery electrodes are fabricated by applying a slurry of particles in suspension to metal foil. If the slurry is too viscous, this can lead to difficulties in the coating process.
Dissolution rates of materials are influenced by the specific surface area of the particulates. Increasing the specific surface area of particles by reducing their size accelerates the dissolution process. This correlation is especially important in pharmaceutical products, where dissolution directly impacts the bioavailability of a drug substance. Agrochemical and detergent manufacturers must also manage particle size to control the dissolution and release rates of active components within a formulation.
Ease of inhalation is an important criterion, both for preventing human inhalation of harmful particles and for optimizing drug deposition in the respiratory tract. For all orally inhaled and nasal drug products (OINDPs), particle size is a critical parameter, with clear size ranges specified for deposition and retention in the nasal cavity and for penetration to different areas of the lungs. In contrast, manufacturers of products such as cleaning materials and hairsprays must control fines to prevent inhalation, making particle size analysis essential to safety testing.
Reaction rates in solid systems are often a function of the specific surface area of the particles involved. The finer the particles, the larger their surface area to volume ratio, which promotes higher reaction rates. This is important in industries as diverse as cement, where particle size impacts the speed of hardening of cement products, and catalyst production, where particle size must be tailored to optimize reaction rates or ensure the effective scavenging of pollutants, and battery manufacture, where particle size must be controlled to balance between power density, charge times and battery durability.
Optical properties such as the light scattering ability of particles are exploited by paint, coatings and pigment manufacturers. The way a particle scatters light depends on its size, so manipulating the size of particles in a surface coating influences performance parameters such as hue and tint strength, product coverage and gloss.
Consumer perception of products such as foodstuffs is often influenced by particle size. For example, the particle size of coffee, and the extent to which it is ground, impact both the flavor released and the time required to brew. A fine particle size in chocolate gives a smooth mouthfeel, frequently perceived as superior to a grainy texture.
The curing properties of materials such as cement are affected by particle size. The curing qualities, and resultant compressive strength of cement, are increased as the particle size decreases due to the increase in surface area. Laser diffraction measures the particle size distribution, which is just as important as average size. If two cement samples have the same average size or surface area then the sample with the narrower size distribution will have a higher compressive strength.
| Particle size | Suspensions, emulsions, dry powders |
|---|---|
| Technology | Laser light scattering |
| Analysis method | Mie and Fraunhofer scattering |
| Data acquisition rate | 10 kHz |
| Typical measurement time | <10 sec |
| Dimensions (W, D, H) | 690mm x 300mm x 450mm |
| Weight | 30 kg |
| Red light source | Max. 4mW He-Ne, 632.8nm |
|---|---|
| Blue light source | None |
| Lens arrangement | Reverse Fourier (convergent beam) |
| Effective focal length | 300 mm |
| Arrangement | Log-spaced array |
|---|---|
| Angular range | 0.015 - 60 degrees |
| Alignment | Automatic |
| Particle size | 0.1 - 2500 µm * |
|---|---|
| Number of size classes | 80 (user adjustable) |
| Accuracy | Better than 0.6% ** |
| Precision / Repeatability | Better than 0.5% variation * |
| Reproducibility | Better than 1% variation * |
| Laser safety | Class 1, IEC60825-1:2007 and CFR Chapter I: Sub-chapterJ: Part 1040 (CDRH) |
|---|---|
| Regulatory testing | RoHS and WEEE compliant CE / FCC compliant Meets requirements of the European Low Voltage directive |
| Power | 100/240 v, 50/60 Hz 50W (no dispersion units connected) 200W maximum (2 dispersion units connected) |
|---|---|
| Humidity | 80% maximum for temperatures up to 31°C, decreasing linearly to 50% at 40°C. Non condensing. |
| Operating temperature (°C) | +5°C to +40°C |
| Product storage temperature | -20°C to +50°C |
| Patents | The Mastersizer optical bench is protected by patents based on applications WO2013038161, WO2013038160 and WO2013038159. |
|---|
| Notes | * Sample and sample preparation dependent
** Accuracy defined for the measurement of monomodal latex standards. This specification accounts for the manufacturer’s uncertainty in the latex size. Sample and sample preparation dependent. |
|---|
Configure the Mastersizer 3000+ Pro for your application and requirements with our range of configuration options below.
Unleash the potential of your data
Until now, instrument data has too often been stuck in manual records, spreadsheets or site-specific servers.
By connecting your Mastersizer 3000+ to our Smart Manager and continually analyzing instrument data in the cloud, you can unleash its full potential.
This is just one of our digital solutions that are part of Malvern Panalytical's Smart Manager.
Get your new Mastersizer 3000+ up and running faster when you choose to smart install.
With comprehensive resources to help you quickly and safely set-up and verify the performance of your new instrument, there’s no need to wait for an engineer to do it for you. What’s more, smart install presents a new training opportunity as you receive full access to exclusive training material.
How does it work?
When you follow the step-by-step video instructions, you could be up and running within 90 minutes of delivery of your new Mastersizer 3000+.
You don't need any specific skills or knowledge to perform a smart installation. Simply follow the instructions provided.
Everything needed to get started is provided with your new instrument – all you need is an internet connection to access the online training.
Exclusive e-learning content
Resources to get you up and running quickly and with confidence include:
Version number: MAN0675-03-DE
Version number: MAN0674-02-SV
Version number: MAN0675-03-EN
Version number: QAS Mastersizer 3000/3000+ (Nov 2024)
Version number: MAN0675-02-ZH
Version number: MAN0674-02-EN
Version number: MAN0481-08-EN
Version number: MAN0479-09-EN
Version number: MAN0674-01-FR
Version number: 01
Version 5.40 is a new feature release. New functionality is introduced through compatibility with the standalone OmniAccess for Mastersizer application for authentication and authorization. The Size Sure measurement mode has received several functional improvements, and a new feedback form has been introduced. This version also includes several bug fixes for Mastersizer Xplorer.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.30 is a new feature release. New functionality is introduced for the SOP Architect feature, available with Mastersizer 3000+ Pro and Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra. This version also includes updates to .NET 8 and Smart Manager v1.6, as well as bug fixes for Mastersizer Xplorer.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.20 is a maintenance release to support the introduction of a new microprocessor within the Mastersizer 3000+ and its accessories.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.10 is a maintenance release. It includes bug fixes for Mastersizer Xplorer, as well as specific updates for the Mastersizer 3000+ Pro.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.03 is a maintenance release.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.02 is a maintenance release. It includes a fix to an issue identified in versions 5.0 and 5.01. If you are using versions 5.0 or 5.01, it is strongly advised that you update to version 5.02.
Version 5.0 rebranded the software as Mastersizer Xplorer and introduced a range of new software features for the Mastersizer 3000+ range.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Important note: A known issue has been flagged for this software version. It is highly encouraged that you read the Software Update Notification (SUN) to understand the impact of this issue and current workarounds before you install. A new software version will be released to resolve the issue.
Version 5.01 is a maintenance release.
Version 5.0 rebranded the software as Mastersizer Xplorer and introduced a range of new software features for the Mastersizer 3000+ product range.
See SUN for further details.
This software is Compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt.11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move on to the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Important note: A known issue has been flagged for this software version. It is highly encouraged that you read the Software Update Notification (SUN) to understand the impact of this issue and current workarounds before you install. A new software version will be released to resolve the issue.
This software is Compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
See SUN for further details.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt.11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move on to the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
|
|
Unmatched uptime and performance
Malvern Panalytical instruments are built to last and good maintenance and care ensure continued peak performance for many years to come.
|
|||
|
|
Advanced analysis and actionable insights
|
|||
|
|
Easy start and streamlined routine operations
|
|||
|
|
Want to speak to a service expert or find the services that are just right for you?
Reach out to our experts and evaluate your services needs and business risks by answering a few questions around the usage of your Malvern Panalytical instrument.
|
|||
|
*Please note that the exact details of our services and their availability are determined by a variety of customer-specific factors, such as product type, product configuration, or location. |
||||
The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro generates the highest quality data for applications needing micron-scale sizing capabilities and the advanced software options of Mastersizer Xplorer.
 Works with OmniTrust: Malvern Panalytical's compliance solution for the regulated environment
Works with OmniTrust: Malvern Panalytical's compliance solution for the regulated environment

The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro uses the technique of laser diffraction to measure the particle size and particle size distribution of materials.
It does this by measuring the intensity of light scattered as a laser beam passes through a dispersed particulate sample.
This data is then analyzed to calculate the size of the particles that created the scattering pattern.
Three main elements enable the system to consistently and reliably deliver the accurate, robust particle sizing data that is central to the effective operation of so many industrial processes.

The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro takes measurements from 0.1 to 2500 µm using a single optical measurement path, making it suitable for an extremely wide range of applications.
The dispersed sample passes though the measurement area of the optical bench, where a laser beam illuminates the particles. A series of detectors then accurately measures the intensity of light scattered by the particles within the sample for red light wavelengths and over a wide range of angles.

The Mastersizer 3000+ Pro comes with a choice of six wet dispersion accessories to handle an extended range of sample volumes and a wide variety of dispersants.
A state-of-the-art dry dispersion system enables rapid and reproducible powder dispersion, even for more fragile materials.
Sample dispersion units ensure that particles are delivered to the measurement area of the optical bench at the correct concentration and in a suitable stable state of dispersion to ensure accurate, reproducible measurements.

Mastersizer Xplorer software meets the growing demand for easy-to-use instruments that deliver excellent results without constant input from experts.
The software controls the system during the measurement process, analyzing scattering data to calculate a particle size distribution. Its intuitive interface guides users through every stage of the process, from selecting a robust method through to routine measurement and result reporting.
In-built expert advice on method development, method performance and results quality reduces training requirements and makes particle size analysis simpler and faster.

Powder flowability is important in maintaining manufacturing efficiency for many processes. Inconsistent powder flow can directly affect product quality variables such as the content uniformity of pharmaceutical dosage forms, or may lead to process variability as powder feed inconsistencies change the effectiveness of particle size reduction processes. Powder flow is a critical consideration in the manufacture of sintered products using additive manufacturing or 3D-printing techniques. Here, poor flow during powder bed deposition may lead to variations in powder bed density, resulting in defects that reduce the strength of the finished part.
Particle size and particle size distribution analysis are critical to understanding the flow properties of a powder, since these characteristics help predict how particles within the powder will pack and lock together. Powders that have a large particle size with a narrow size distribution tend to exhibit good flowability. Those with a small particle size, or a broad particle size distribution, tend towards poorer flowability because of the greater surface area of contact that exists between the particles and the ability of the fine particles present to fill the voids.
The packing density of particles influences the success of many processes, including mold-filling in ceramic and metal component production, powder coating, and the solids loading of suspensions. The way that particles pack together is a function of both their size and size distribution. Larger particles pack less efficiently than smaller ones, creating bigger voids. Broadening the particle size distribution improves packing efficiency by allowing smaller particles to pack the spaces between larger ones. Minimizing voidage is crucial to producing flaw-free sintered components. In powder coating, close packing enables efficient melting at lower temperatures, giving more time for cross-linking reactions between polymer particles for a better finish.
Particle packing also influences the rheology of suspensions, principally their viscosity. A mix of large and small particles has the least impact on the viscosity of the system because of their greater packing efficiency, a phenomenon that can be exploited to increase the solids loading of suspensions such as paints and ceramics.
The stability of suspensions and emulsions used and produced in industries such as pharmaceuticals and foods is important in ensuring product efficacy, acceptability, and success. Dispersion stability and gravitational separation are both key elements.
Dispersion stability: Achieving a stable dispersion requires control of the forces of adhesion and cohesion that exist between particles within a medium. These forces can lead to flocculation of emulsions or the creation of agglomerates within suspensions and powders. The risk of poor dispersion stability increases with decreasing particle size and can significantly impact processing. It may lead to powder conveyance issues within manufacturing processes, or problems with final product performance, such as the formation of agglomerates that give rise to imperfections in coatings and paints. Particle size and particle size distribution analysis is used in the management of dispersion stability risk and to identify the impact of stability problems on product performance and acceptance.
Gravitational separation: Improving the stability of a suspension or emulsion to gravitational separation relies on balancing the gravitational pull on the particles, a function of particle size and density, with the up-thrust of the suspending fluid, which depends on viscosity. In emulsions, particle size analysis is used to assess the likelihood of creaming, to which larger droplets are prone, and to monitor stability to flocculation and coalescence over time. Since droplet size and the degree of flocculation may also affect characteristics such as the mouthfeel of a food or the viscosity of a drink, particle size should be measured routinely when optimizing and manufacturing emulsion formulations.
The viscosity and flow of suspensions and slurries depend on different physical properties, including particle size and particle size distribution. If particle size decreases (for a constant volume fraction) and/or the size distribution increases, the sample viscosity will increase and the sample will flow less readily. Viscosity is important for many applications such as paints, cosmetics and battery manufacture. Take batteries, for example, where the battery electrodes are fabricated by applying a slurry of particles in suspension to metal foil. If the slurry is too viscous, this can lead to difficulties in the coating process.
Dissolution rates of materials are influenced by the specific surface area of the particulates. Increasing the specific surface area of particles by reducing their size accelerates the dissolution process. This correlation is especially important in pharmaceutical products, where dissolution directly impacts the bioavailability of a drug substance. Agrochemical and detergent manufacturers must also manage particle size to control the dissolution and release rates of active components within a formulation.
Ease of inhalation is an important criterion, both for preventing human inhalation of harmful particles and for optimizing drug deposition in the respiratory tract. For all orally inhaled and nasal drug products (OINDPs), particle size is a critical parameter, with clear size ranges specified for deposition and retention in the nasal cavity and for penetration to different areas of the lungs. In contrast, manufacturers of products such as cleaning materials and hairsprays must control fines to prevent inhalation, making particle size analysis essential to safety testing.
Reaction rates in solid systems are often a function of the specific surface area of the particles involved. The finer the particles, the larger their surface area to volume ratio, which promotes higher reaction rates. This is important in industries as diverse as cement, where particle size impacts the speed of hardening of cement products, and catalyst production, where particle size must be tailored to optimize reaction rates or ensure the effective scavenging of pollutants, and battery manufacture, where particle size must be controlled to balance between power density, charge times and battery durability.
Optical properties such as the light scattering ability of particles are exploited by paint, coatings and pigment manufacturers. The way a particle scatters light depends on its size, so manipulating the size of particles in a surface coating influences performance parameters such as hue and tint strength, product coverage and gloss.
Consumer perception of products such as foodstuffs is often influenced by particle size. For example, the particle size of coffee, and the extent to which it is ground, impact both the flavor released and the time required to brew. A fine particle size in chocolate gives a smooth mouthfeel, frequently perceived as superior to a grainy texture.
The curing properties of materials such as cement are affected by particle size. The curing qualities, and resultant compressive strength of cement, are increased as the particle size decreases due to the increase in surface area. Laser diffraction measures the particle size distribution, which is just as important as average size. If two cement samples have the same average size or surface area then the sample with the narrower size distribution will have a higher compressive strength.
| Particle size | Suspensions, emulsions, dry powders |
|---|---|
| Technology | Laser light scattering |
| Analysis method | Mie and Fraunhofer scattering |
| Data acquisition rate | 10 kHz |
| Typical measurement time | <10 sec |
| Dimensions (W, D, H) | 690mm x 300mm x 450mm |
| Weight | 30 kg |
| Red light source | Max. 4mW He-Ne, 632.8nm |
|---|---|
| Blue light source | None |
| Lens arrangement | Reverse Fourier (convergent beam) |
| Effective focal length | 300 mm |
| Arrangement | Log-spaced array |
|---|---|
| Angular range | 0.015 - 60 degrees |
| Alignment | Automatic |
| Particle size | 0.1 - 2500 µm * |
|---|---|
| Number of size classes | 80 (user adjustable) |
| Accuracy | Better than 0.6% ** |
| Precision / Repeatability | Better than 0.5% variation * |
| Reproducibility | Better than 1% variation * |
| Laser safety | Class 1, IEC60825-1:2007 and CFR Chapter I: Sub-chapterJ: Part 1040 (CDRH) |
|---|---|
| Regulatory testing | RoHS and WEEE compliant CE / FCC compliant Meets requirements of the European Low Voltage directive |
| Power | 100/240 v, 50/60 Hz 50W (no dispersion units connected) 200W maximum (2 dispersion units connected) |
|---|---|
| Humidity | 80% maximum for temperatures up to 31°C, decreasing linearly to 50% at 40°C. Non condensing. |
| Operating temperature (°C) | +5°C to +40°C |
| Product storage temperature | -20°C to +50°C |
| Patents | The Mastersizer optical bench is protected by patents based on applications WO2013038161, WO2013038160 and WO2013038159. |
|---|
| Notes | * Sample and sample preparation dependent
** Accuracy defined for the measurement of monomodal latex standards. This specification accounts for the manufacturer’s uncertainty in the latex size. Sample and sample preparation dependent. |
|---|
Configure the Mastersizer 3000+ Pro for your application and requirements with our range of configuration options below.
Unleash the potential of your data
Until now, instrument data has too often been stuck in manual records, spreadsheets or site-specific servers.
By connecting your Mastersizer 3000+ to our Smart Manager and continually analyzing instrument data in the cloud, you can unleash its full potential.
This is just one of our digital solutions that are part of Malvern Panalytical's Smart Manager.
Get your new Mastersizer 3000+ up and running faster when you choose to smart install.
With comprehensive resources to help you quickly and safely set-up and verify the performance of your new instrument, there’s no need to wait for an engineer to do it for you. What’s more, smart install presents a new training opportunity as you receive full access to exclusive training material.
How does it work?
When you follow the step-by-step video instructions, you could be up and running within 90 minutes of delivery of your new Mastersizer 3000+.
You don't need any specific skills or knowledge to perform a smart installation. Simply follow the instructions provided.
Everything needed to get started is provided with your new instrument – all you need is an internet connection to access the online training.
Exclusive e-learning content
Resources to get you up and running quickly and with confidence include:
Version number: MAN0675-03-DE
Version number: MAN0674-02-SV
Version number: MAN0675-03-EN
Version number: QAS Mastersizer 3000/3000+ (Nov 2024)
Version number: MAN0675-02-ZH
Version number: MAN0674-02-EN
Version number: MAN0481-08-EN
Version number: MAN0479-09-EN
Version number: MAN0674-01-FR
Version number: 01
Version 5.40 is a new feature release. New functionality is introduced through compatibility with the standalone OmniAccess for Mastersizer application for authentication and authorization. The Size Sure measurement mode has received several functional improvements, and a new feedback form has been introduced. This version also includes several bug fixes for Mastersizer Xplorer.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.30 is a new feature release. New functionality is introduced for the SOP Architect feature, available with Mastersizer 3000+ Pro and Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra. This version also includes updates to .NET 8 and Smart Manager v1.6, as well as bug fixes for Mastersizer Xplorer.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.20 is a maintenance release to support the introduction of a new microprocessor within the Mastersizer 3000+ and its accessories.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.10 is a maintenance release. It includes bug fixes for Mastersizer Xplorer, as well as specific updates for the Mastersizer 3000+ Pro.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.03 is a maintenance release.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Version 5.02 is a maintenance release. It includes a fix to an issue identified in versions 5.0 and 5.01. If you are using versions 5.0 or 5.01, it is strongly advised that you update to version 5.02.
Version 5.0 rebranded the software as Mastersizer Xplorer and introduced a range of new software features for the Mastersizer 3000+ range.
See Software Update Notification (SUN) document for further details.
This software is compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+ Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt. 11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move onto the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Important note: A known issue has been flagged for this software version. It is highly encouraged that you read the Software Update Notification (SUN) to understand the impact of this issue and current workarounds before you install. A new software version will be released to resolve the issue.
Version 5.01 is a maintenance release.
Version 5.0 rebranded the software as Mastersizer Xplorer and introduced a range of new software features for the Mastersizer 3000+ product range.
See SUN for further details.
This software is Compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt.11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move on to the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
Important note: A known issue has been flagged for this software version. It is highly encouraged that you read the Software Update Notification (SUN) to understand the impact of this issue and current workarounds before you install. A new software version will be released to resolve the issue.
This software is Compatible with Mastersizer range: Mastersizer 3000+ Ultra, Mastersizer 3000+ Pro, Mastersizer 3000+Lab, Mastersizer 3000 and Mastersizer 3000E.
See SUN for further details.
Note: This software no longer supports the use of the Malvern Access Control (MAC) or 21CFR Pt.11 feature key. This functionality is now provided via OmniTrust. Users that wish to move on to the OmniTrust platform are now supported to retain access to their existing audit trail information. For more information, refer to the SUN document before installing the software or contact your Malvern Panalytical representative.
|
|
Unmatched uptime and performance
Malvern Panalytical instruments are built to last and good maintenance and care ensure continued peak performance for many years to come.
|
|||
|
|
Advanced analysis and actionable insights
|
|||
|
|
Easy start and streamlined routine operations
|
|||
|
|
Want to speak to a service expert or find the services that are just right for you?
Reach out to our experts and evaluate your services needs and business risks by answering a few questions around the usage of your Malvern Panalytical instrument.
|
|||
|
*Please note that the exact details of our services and their availability are determined by a variety of customer-specific factors, such as product type, product configuration, or location. |
||||

Trusted the world over to deliver robust, reliable data, customized to meet your needs, all wrapped up in a user-friendly package. No wonder it’s the world’s favorite.