Energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF)
Malvern Panalytical Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence EDXRF Spectrometers
Malvern Panalytical Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence EDXRF Spectrometers
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry is a non-destructive analytical technique used to obtain elemental information from different types of materials.
It is employed in many industries and applications including: cement production, glass production, mining, mineral beneficiation, iron, steel and non-ferrous metals, petroleum and petrochemicals, polymers and related industries, forensics, pharmaceuticals, healthcare products, environmental, food and cosmetics.
Spectrometer systems are generally divided into two main groups: wavelength dispersive systems (WDXRF) and energy dispersive systems (EDXRF). The difference between the two lies in the detection system.
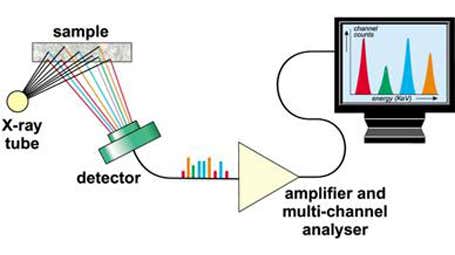
The basic concept of all spectrometers is a radiation source, a sample and a detection system. In EDXRF spectrometers, the X-ray tube acting as a source irradiates a sample directly, and the fluorescence coming from the sample is measured with an energy dispersive detector. This detector is able to measure the different energies of the characteristic radiation coming directly from the sample. The detector can separate the radiation from the sample into the radiation from the different elements present in the sample. This separation is called dispersion.

RevontiumEnergy-dispersive XRF, designed for demanding labs. Economical footprint. 4x speed. No compromise on precision. |

Epsilon 1Small, powerful and portable XRF analyzer |

Epsilon XflowDirect insight into your liquid process parameters |

Epsilon 4Fast and accurate at-line elemental analysis |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|