Cu-base
FP for elemental analysis of a wide range of Cu alloys

FP for elemental analysis of a wide range of Cu alloys

‘Copper-base’ (Cu-base) is a term used to describe a range of alloys where Cu is the principal component. In order to make the materials suitable for different applications (e.g. the manufacture of coinage, bells, a wide range of mechanical equipment and electrical wiring), Cu is normally alloyed with elements such as Sn, Zn, Ni, Al, and Pb. During the production process fast elemental analysis is needed to minimize errors in production and maximize production yield.
The Cu-base-FP package, including applicable calibration standards, covers the analysis of this wide range of Cu alloys by using Malvern Panalytical’s Fundamental Parameter (FP) model.
The Cu-base-FP module comes with a suite of carefully selected certified reference samples and an application template for easy method setup.
The module allows very accurate and precise analysis of a wide range of Cu-based materials:

The Cu-base-FP module is designed to be used in combination with Malvern Panalytical’s FP algorithm used in the SuperQ software, which calculates matrix corrections from the theoretical principles governing the physics of X-rays. As such, FP models have a significant advantage over more traditional influence coefficient-based matrix corrections, e.g. theoretical alphas or empirical corrections. Unlike theoretical alphas calculations, the FP model calculates matrix corrections that are specific to each sample. This enables accurate analyses over wide concentration ranges and many different sample types.
The Cu-base module comprises of:
The Cu-base-FP module and setup samples are designed to be used in combination with Malvern Panalytical WD XRF instruments like Zetium. Certain hardware requirements apply. The module can be delivered as a pre-calibrated solution on new systems, but can also be deployed on existing instruments running SuperQ software.
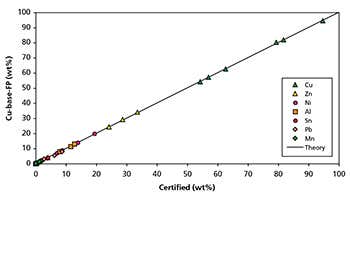
The elements and concentrations covered are listed in the table below:
| Element | Concentration range (wt%) |
|---|---|
| Mg | < LLD – 0.3 |
| Al | < LLD – 13 |
| Si | < LLD – 0.6 |
| P | 0.001 – 1 |
| S | 0.0013 – 0.1 |
| Cr | 0.0013 – 1 |
| Mn | < LLD – 2.3 |
| Fe | 0.003 – 5.6 |
| Co | 0.012 – 0.3 |
| Ni | 0.007 – 33 |
| Cu | 54.4 – 96 |
| Zn | 0.013 – 43 |
| As | < LLD – 0.3 |
| Sn | 0.006 – 17 |
| Sb | 0.005 – 0.5 |
| Pb | 0.005 – 21 |
| Bi | < LLD – 2 |
Note: If the certified concentration is lower than the LLD value, the term < LLD has been used to indicate the lower limit of the concentration range